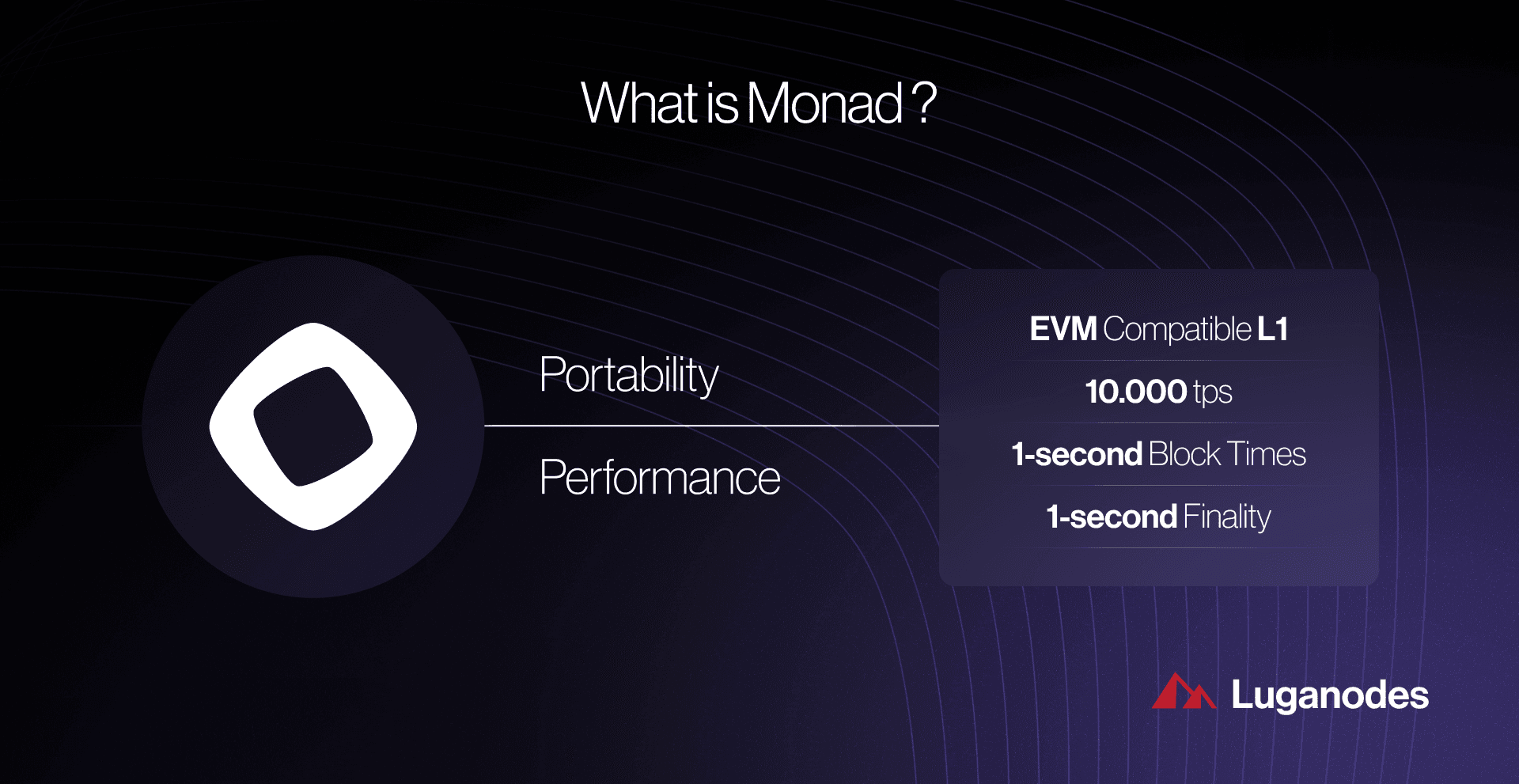
In the rapidly evolving landscape of decentralized finance (DeFi), transaction throughput and scalability remain core challenges for EVM-compatible blockchains. While Ethereum’s architecture has become the industry standard, its sequential execution model limits throughput to approximately 10-15 transactions per second (TPS), creating bottlenecks and high fees during periods of network congestion. Enter Monad: a high-performance EVM-compatible Layer 1 blockchain that reimagines transaction processing through parallelization, unlocking up to 10,000 TPS with near-instantaneous finality. This architectural leap positions Monad as a transformative force for DeFi applications, enabling seamless user experiences and supporting the next generation of complex financial primitives.

Breaking Free from Sequential Constraints: The Monad Approach
At the heart of Monad’s innovation lies a fundamental departure from the traditional EVM execution paradigm. Where Ethereum and most EVM-compatible chains process transactions one after another, Monad employs parallel transaction execution. By analyzing incoming transactions to identify those that do not conflict with each other, Monad orchestrates simultaneous processing across multiple threads. This approach is not a mere optimization – it is a structural overhaul that multiplies throughput without sacrificing security or compatibility.
The implications for DeFi are profound. High-frequency trading, automated market makers, lending protocols, and cross-chain bridges all benefit from reduced latency and increased capacity. Instead of waiting in line behind unrelated transactions, DeFi operations on Monad can be confirmed within seconds – regardless of how busy the network becomes.
The Pillars of Performance: Deferred Execution and MonadDB
Monad’s performance gains are underpinned by two core innovations:
- Deferred Execution: Unlike conventional blockchains that immediately execute transactions during consensus, Monad separates ordering from execution. Validators first agree on transaction order using the MonadBFT consensus mechanism, then independently execute transactions in parallel. This decoupling streamlines consensus communication and accelerates block finality to around one second.
- MonadDB Storage System: To fully realize parallel processing, storage must keep pace. Traditional blockchain databases become I/O bottlenecks under heavy load. MonadDB solves this with asynchronous disk operations that allow multiple read/write actions simultaneously, eliminating delays and supporting true high-throughput environments.
Together, these features deliver not just raw speed but also reliability and state consistency – essential attributes for mission-critical DeFi protocols.
Key Benefits of Monad EVM Parallelization for DeFi Developers
-

Massive Transaction Throughput: Monad’s parallel execution architecture enables up to 10,000 transactions per second (TPS), far surpassing the 10–15 TPS typical of traditional EVM blockchains. This allows DeFi platforms to scale to millions of users without congestion.
-
Ultra-Low Latency and Fast Finality: With ~1-second block finality enabled by MonadBFT, DeFi applications can offer near-instant transaction confirmations, improving user experience and enabling latency-sensitive protocols like DEXs and derivatives platforms.
-
Significantly Reduced Transaction Fees: Enhanced throughput and efficient resource utilization lower network congestion, resulting in substantially reduced gas costs for DeFi users and protocols.
-

Seamless EVM Compatibility: Monad is fully EVM-compatible, allowing DeFi developers to deploy existing Ethereum smart contracts and use familiar tooling without modification, accelerating time-to-market.
-

Production-Grade Security and Decentralization: Monad’s architecture, including MonadBFT and MonadDB, delivers robust security guarantees and true decentralization, ensuring DeFi protocols remain trustless and resilient.
-

Enhanced Scalability for Complex DeFi Protocols: By decoupling transaction ordering from execution and leveraging parallelism, Monad enables more complex and computation-intensive DeFi applications to operate efficiently and at scale.
EVM Compatibility Without Compromise
A critical advantage for developers is that Monad maintains full Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility. Existing Solidity smart contracts can be deployed natively without modification, ensuring seamless migration or multi-chain strategies for established DeFi projects. This compatibility extends to tooling, wallets, and infrastructure – dramatically lowering barriers to adoption while providing access to next-level performance metrics.
The result is an ecosystem where innovation is bounded only by imagination rather than technical limitations. As demand for low-latency financial services grows globally, platforms built on Monad can scale horizontally without encountering the typical trade-offs between decentralization, security, and speed.
Developers and enterprises seeking to deploy high-performance DeFi applications are now empowered to do so without the friction of rewriting code or compromising on decentralization. Monad’s meticulous adherence to the EVM specification ensures that every Solidity contract, every familiar tool, and every integration pattern remains intact – yet runs at a scale previously unimaginable in the EVM landscape. This makes Monad an attractive migration path for existing protocols as well as a fertile ground for new DeFi primitives that demand real-time settlement and microsecond-level responsiveness.
Impact on DeFi: Efficiency, User Experience, and Ecosystem Growth
The practical impact of Monad’s parallelized EVM architecture is already visible in early deployments and testnet benchmarks. Transaction fees are dramatically reduced due to increased network capacity. Confirmation times drop to near one second, enabling seamless interactions for end users – from instant swaps on decentralized exchanges to real-time collateral adjustments in lending platforms. These improvements not only enhance user experience but also unlock entirely new categories of financial products that require high throughput and low latency.
For liquidity providers, arbitrageurs, and institutional players, Monad’s architecture mitigates front-running risks and slippage by minimizing mempool congestion and ensuring deterministic ordering via deferred execution. The result is a fairer, more transparent marketplace where capital efficiency is maximized.
Furthermore, the scalability unlocked by Monad’s 10,000 TPS throughput supports ecosystem growth without sacrificing decentralization or security – two pillars often compromised in alternative scaling solutions. As more projects recognize these advantages, network effects are likely to accelerate: composability between protocols remains seamless thanks to EVM compatibility, while the underlying infrastructure scales effortlessly with demand.
Technical Deep Dive: How Parallelization Works
At a technical level, Monad’s execution engine dynamically analyzes incoming transactions for data dependencies. Transactions that interact with independent state variables are grouped into batches for simultaneous execution across multiple CPU cores. This process is orchestrated by sophisticated scheduling algorithms that optimize resource utilization while preserving deterministic outcomes – a critical requirement for blockchain consensus.
The custom-built MonadDB storage layer further amplifies these gains by supporting concurrent disk operations. Unlike traditional blockchains where database locks can stall throughput under load, MonadDB leverages asynchronous I/O primitives so that reads and writes never become a bottleneck. This synergy between computation and storage sets a new bar for what is possible with EVM-compatible blockchains.
What This Means for Web3 Builders
For teams building next-generation DeFi protocols or migrating high-velocity dApps from Ethereum Mainnet or other L1s/L2s, Monad offers:
Key Benefits of Monad EVM Parallelization for DeFi Developers
-

Unmatched Transaction Throughput: Monad achieves up to 10,000 transactions per second (TPS) through parallel execution, far surpassing traditional EVM chains like Ethereum, which supports around 10 TPS. This enables DeFi platforms to handle massive user volumes and complex operations without congestion.
-

Ultra-Low Latency and Fast Finality: With ~1-second block finality, Monad ensures that DeFi transactions are confirmed almost instantly, greatly improving user experience and enabling real-time financial services.
-

Reduced Transaction Fees: The high throughput and efficient architecture of Monad lead to lower transaction fees for users and developers, making DeFi applications more accessible and cost-effective.
-
Seamless EVM Compatibility: Monad is fully EVM-compatible, allowing DeFi developers to deploy existing Ethereum smart contracts and dApps without modification, leveraging established tools and developer ecosystems.
-
Scalable Infrastructure for Complex DeFi Applications: Monad’s parallel execution and custom MonadDB storage system eliminate traditional I/O bottlenecks, supporting the development of advanced DeFi protocols that require high performance and scalability.
-

Production-Grade Security and Decentralization: Built with MonadBFT consensus (based on HotStuff), Monad offers robust security and true decentralization, ensuring trustless and resilient DeFi operations.
This paradigm shift isn’t just about raw numbers – it’s about unlocking new design space for permissionless finance at global scale.
“Monad’s parallelized EVM is not just an incremental improvement; it’s a categorical leap that redefines what’s possible for decentralized finance. “
As DeFi continues its march toward mainstream adoption, chains like Monad will underpin the next wave of innovation by removing historical bottlenecks without sacrificing the core values of openness and security. For developers committed to building at the frontier of performance and composability, Monad represents both an evolutionary step forward and an invitation to redefine what the future of finance can be.






